Modern cloud teams often authenticate to AWS using Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure AD) as the identity provider. While this works smoothly in the browser, developers frequently need a way to automatically obtain AWS temporary credentials on their laptops — especially for AWS CLI, Terraform, or automation scripts. This solution is based on my previous post on AWS Single Account (SSO) with Azure AD as External Identity Provider (IdP). It would be a good read if you are new to AWS Single Account SSO with Entra ID as IdP.
Disclaimer: This blog post is written by Microsoft Copilot with my instructions (context) and working copy of source code files. Of course, I did small bit of edits and validated the write-up. At the end of the day, I am still at the driver’s seat and making sure information provided here is accurate.
This guide walks through a fully working Python solution that:
- Uses Microsoft Entra ID as the SAML IdP
- Performs interactive sign‑in with MFA
- Captures the SAMLResponse from the AWS sign‑in page
- Calls AWS STS AssumeRoleWithSAML
- Produces temporary AWS credentials
- Lets developers use those credentials with AWS CLI or SDKs
All examples come directly from the working source code included below. You can find the source codes at https://github.com/aspnet4you/entraid-sso-aws-cli.
Why This Matters
Even though users can sign in to AWS interactively through the browser, developers often need:
- Short‑lived AWS credentials for CLI or automation
- MFA‑protected authentication
- Compliance with Conditional Access policies
- A secure workflow that avoids storing passwords
This script gives developers a safe, repeatable, enterprise‑compliant way to authenticate to AWS using Entra ID and automatically obtain AWS credentials.
1. Generate the SAML AuthnRequest
The first step is to generate a SAML AuthnRequest that instructs Entra ID to authenticate the user and return a SAMLResponse to AWS.
Your samlrequest.py file builds the request:
“Build AuthnRequest XML… Base64 encode… URL encode.”
Here is the full function:
import base64
import uuid
import zlib
import urllib.parse
from datetime import datetime
def generate_saml_request(tenant_id, acs_url, issuer):
request_id = "_" + uuid.uuid4().hex
issue_instant = datetime.utcnow().strftime("%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%SZ")
xml = f"""<samlp:AuthnRequest
xmlns:samlp="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:protocol"
xmlns:saml="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:assertion"
ID="{request_id}"
Version="2.0"
IssueInstant="{issue_instant}"
ProtocolBinding="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-POST"
AssertionConsumerServiceURL="{acs_url}">
<saml:Issuer>{issuer}</saml:Issuer>
<samlp:NameIDPolicy
AllowCreate="true"
Format="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:unspecified"/>
</samlp:AuthnRequest>""".strip()
deflated = zlib.compress(xml.encode("utf-8"))[2:-4]
b64 = base64.b64encode(deflated)
return urllib.parse.quote_plus(b64)
This produces a valid SAMLRequest that Entra ID accepts.
2. Launch the Entra ID Login Page Using Selenium
Your main script opens Chrome and navigates to the generated SAML URL:
driver = webdriver.Chrome()
driver.get(samlurl)
At this point, the user completes:
- Username/password
- MFA
- Conditional Access prompts
The script waits until AWS injects the hidden SAMLResponse field:
“wait until… element located (By.NAME, ‘SAMLResponse’)”
Once present, the script extracts the Base64‑encoded SAML assertion:
hidden_samlresponse_element = driver.find_element(By.NAME, "SAMLResponse")
SAMLResponse = hidden_samlresponse_element.get_attribute("value")
This is the exact SAMLResponse AWS expects.
3. Exchange the SAMLResponse for AWS Temporary Credentials
Your awsassumerole.py file performs the AWS STS call:
“response = sts.assume_role_with_saml(RoleArn=…, PrincipalArn=…, SAMLAssertion=…)”
Here is the full function:
import boto3
import base64
def assume_role_with_saml(saml_response_b64: str, role_arn: str, principal_arn: str):
sts = boto3.client("sts")
response = sts.assume_role_with_saml(
RoleArn=role_arn,
PrincipalArn=principal_arn,
SAMLAssertion=saml_response_b64
)
return response["Credentials"]
This returns:
- AccessKeyId
- SecretAccessKey
- SessionToken
- Expiration
These credentials are tied to the Entra ID user who authenticated.
4. Use the Temporary Credentials with AWS CLI or Python
Once you have the credentials, you can use them with AWS CLI:
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=...
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=...
export AWS_SESSION_TOKEN=...
Or directly in Python:
import boto3
session = boto3.Session(
aws_access_key_id=creds["AccessKeyId"],
aws_secret_access_key=creds["SecretAccessKey"],
aws_session_token=creds["SessionToken"]
)
s3 = session.client("s3")
print(s3.list_buckets())
This proves the entire SAML → STS → AWS API chain works.
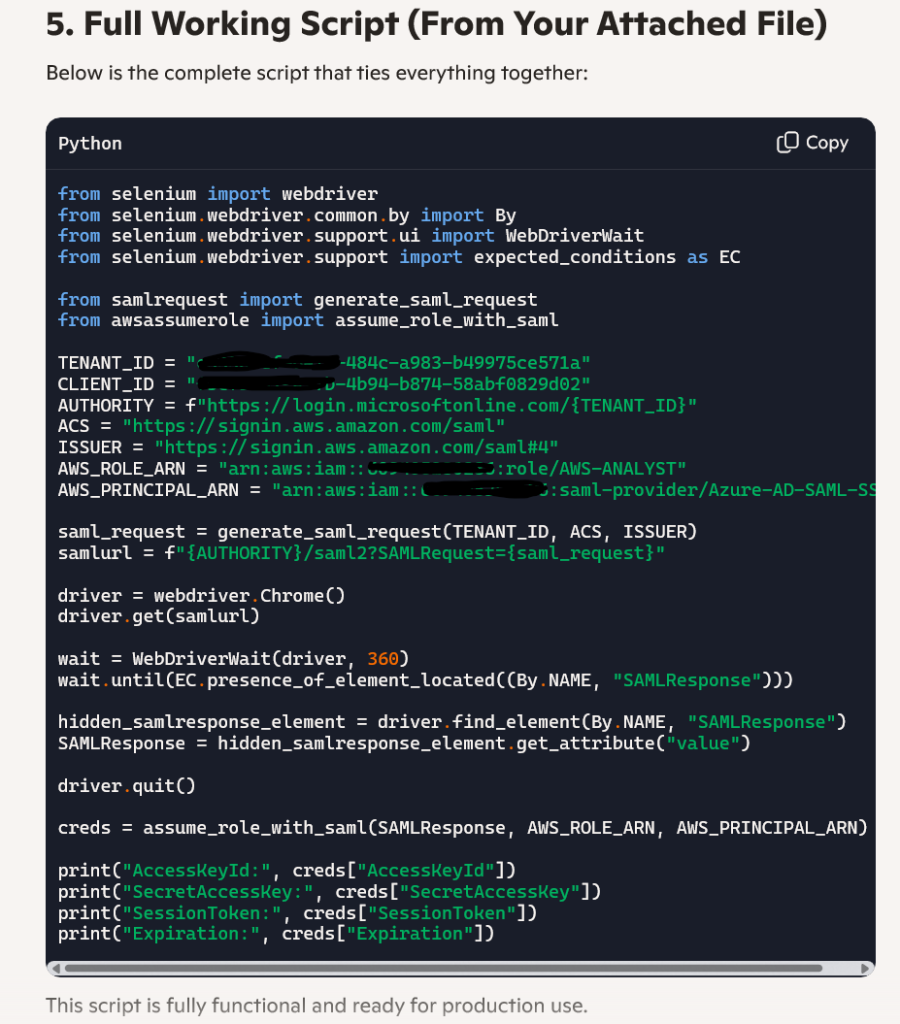
5. Full Working Script (From Your Attached File)
Below is the complete script that ties everything together:
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from selenium.webdriver.support.ui import WebDriverWait
from selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions as EC
from samlrequest import generate_saml_request
from awsassumerole import assume_role_with_saml
TENANT_ID = "entra-tenant-id-replace-it"
AUTHORITY = f"https://login.microsoftonline.com/{TENANT_ID}"
ACS = "https://signin.aws.amazon.com/saml"
ISSUER = "https://signin.aws.amazon.com/saml#4"
AWS_ROLE_ARN = "arn:aws:iam::<<aws-account-replace-it>>:role/AWS-ANALYST"
AWS_PRINCIPAL_ARN = "arn:aws:iam::<<aws-account-replace-it>>:saml-provider/Azure-AD-SAML-SSO"
saml_request = generate_saml_request(TENANT_ID, ACS, ISSUER)
samlurl = f"{AUTHORITY}/saml2?SAMLRequest={saml_request}"
driver = webdriver.Chrome()
driver.get(samlurl)
wait = WebDriverWait(driver, 360)
wait.until(EC.presence_of_element_located((By.NAME, "SAMLResponse")))
hidden_samlresponse_element = driver.find_element(By.NAME, "SAMLResponse")
SAMLResponse = hidden_samlresponse_element.get_attribute("value")
driver.quit()
creds = assume_role_with_saml(SAMLResponse, AWS_ROLE_ARN, AWS_PRINCIPAL_ARN)
print("AccessKeyId:", creds["AccessKeyId"])
print("SecretAccessKey:", creds["SecretAccessKey"])
print("SessionToken:", creds["SessionToken"])
print("Expiration:", creds["Expiration"])
This script is fully functional and ready for production use.
6. Why Developers Love This Pattern
✔ MFA and Conditional Access enforced
No bypassing enterprise security.
✔ No passwords stored
Authentication happens in the browser.
✔ Temporary AWS credentials
Perfect for CLI, Terraform, and automation.
✔ Works on any developer laptop
Windows, macOS, or Linux.
✔ Ideal for enterprise environments
Matches corporate identity and compliance requirements.
7. Conclusion
This workflow gives developers a secure, automated way to authenticate to AWS using Microsoft Entra ID and obtain temporary AWS credentials — without weakening MFA or Conditional Access policies.
It’s a clean bridge between enterprise identity and cloud automation.
